Alternative Angioplasty
Angioplasty, commonly referred to as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels supplying the heart. While angioplasty is highly effective for many patients, alternative treatments or approaches may be considered depending on the patient's specific condition, overall health, or preferences. Here are detailed alternatives to angioplasty:
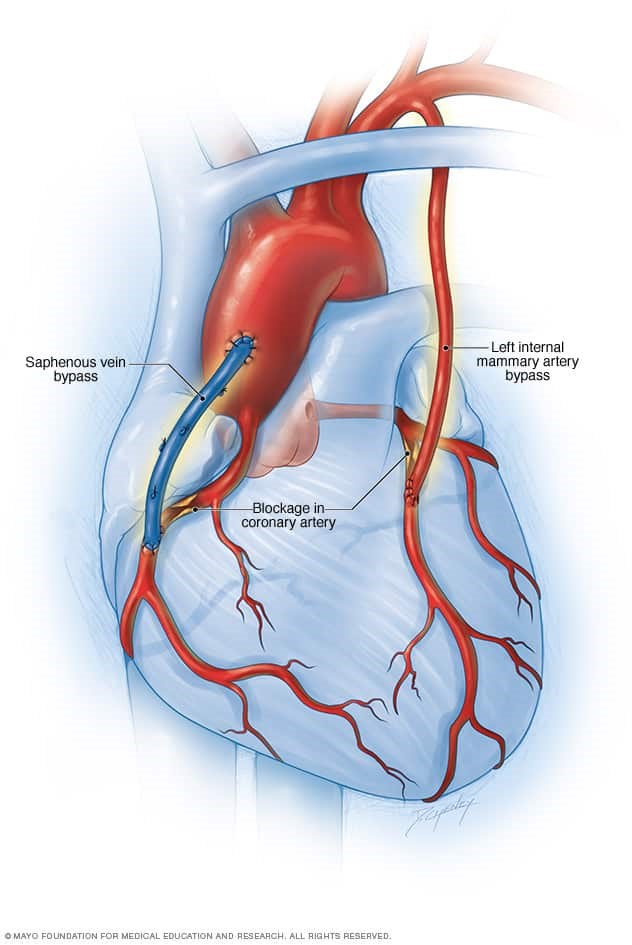
1. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
- What it is: A surgical procedure where a healthy blood vessel (from the leg, arm, or chest) is used to bypass the blocked coronary arteries.
- When it's preferred:
- Multiple blockages in major coronary arteries.
- Severe narrowing or complete occlusion of arteries.
- Diabetes or other comorbidities that make angioplasty less effective.
- Advantages:
- Long-lasting solution for complex or widespread coronary artery disease.
- Improved blood flow across multiple blocked arteries.
- Drawbacks:
- Invasive surgery with a longer recovery time.
- Higher risk of complications compared to angioplasty.
2. Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
- What it is: A non-invasive procedure that uses cuffs on the legs to improve blood flow to the heart by increasing blood pressure during diastole (heart relaxation phase).
- When it's preferred:
- Patients with chronic angina who are not candidates for angioplasty or CABG.
- Those seeking a non-invasive approach.
- Advantages:
- Painless, outpatient procedure.
- Improves symptoms of angina and may promote the growth of new collateral blood vessels.
- Drawbacks:
- Requires multiple sessions (typically 35–40).
- May not be effective for all patients.
3. Lifestyle Changes and Medical Therapy
- What it is: Comprehensive management of coronary artery disease through medications and lifestyle modifications.
- When it's preferred:
- Early-stage coronary artery disease or mild symptoms.
- Patients who prefer non-procedural approaches.
- Components:
- Medications:
- Statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs).
- Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers (to reduce heart workload and improve blood flow).
- Antiplatelet drugs like aspirin (to prevent clot formation).
- Lifestyle modifications:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet (low in saturated fats, high in fruits and vegetables).
- Regular exercise tailored to the individual’s capacity.
- Smoking cessation and weight management.
- Medications:
- Advantages:
- Non-invasive and cost-effective.
- Reduces cardiovascular risk factors over the long term.
- Drawbacks:
- May take longer to see improvement.
- Requires strong patient commitment.
4. Atherectomy
- What it is: A minimally invasive procedure that removes plaque buildup from the artery using a catheter with a rotating blade or laser.
- When it's preferred:
- When calcified plaques or hard blockages are present.
- Cases where stenting is not feasible due to arterial structure.
- Advantages:
- Targets specific blockages without stenting.
- Drawbacks:
- Higher risk of artery damage.
- Less commonly performed than angioplasty.