Eardrum Transplantation and Alternative Treatment
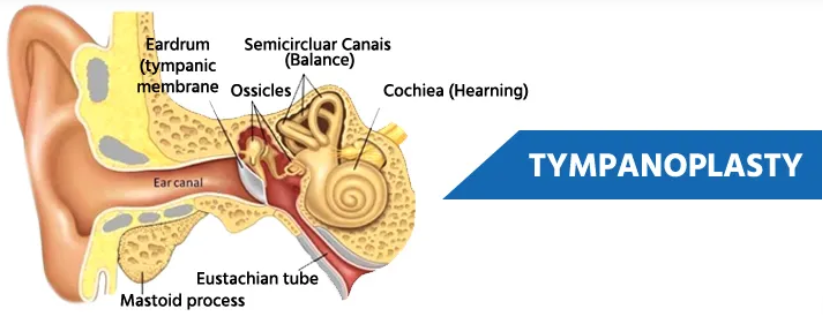
Hearing and balance depend on the human ear, a sensitive and intricate organ. Sound waves are transferred from the outer ear to the middle ear by the eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, which is essential to the auditory process. Hearing loss, pain, and recurring infections can arise from damage to the eardrum caused by a variety of factors, such as trauma, persistent infections, or congenital flaws. A damaged eardrum can be replaced or repaired surgically via eardrum transplantation, sometimes referred to as tympanic membrane transplantation or tympanoplasty. The eardrum transplant procedure and associated alternative therapies are thoroughly examined in this essay, which covers both traditional medical methods and homeopathic medicines.
Eardrum Transplantation
A surgical procedure called eardrum transplantation is used to replace or repair the tympanic membrane. Patients with large perforations or persistent damage that has not healed on its own are usually advised to have the operation. If the middle ear bones (ossicles) are injured, tympanoplasty, the most popular kind of eardrum transplantation, may also entail their restoration or repair.
The choice of graft material is the first step in the surgical procedure. The graft is often taken from the patient's own body, such as the perichondrium from the ear cartilage or the fascia from the temporalis muscle. The surgeon carefully positions the prepared graft over the eardrum perforation, making sure it is properly aligned to restore the integrity of the membrane. In addition to enhancing hearing, the operation seeks to stop repeated ear infections and other issues brought on by a broken eardrum.
Tympanoplasty typically has a high success rate, with the majority of patients reporting notable aural and symptom relief benefits. In order to promote appropriate healing and prevent infection, post-operative care is essential, which includes minimizing water exposure and according to the surgeon's instructions.
Alternative Conventional Treatments
Other standard therapies could be enough for those with less severe eardrum damage. Myringoplasty is a less complex surgical surgery that uses comparable grafting procedures to heal minor eardrum holes. Compared to tympanoplasty, this treatment is less invasive and usually requires a shorter recovery period.
Small holes may occasionally heal on their own without the need for surgery. An ENT (ear, nose, and throat) expert must provide routine monitoring throughout this time to guarantee appropriate healing and handle any possible issues. Furthermore, treating underlying issues like eustachian tube dysfunction can greatly speed up the healing process. Nasal decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, or balloon dilation techniques to enhance drainage and airflow are possible treatments for eustachian tube dysfunction.
Hearing aids provide a non-invasive option for those who suffer from hearing loss as a result of eardrum injury but are not good candidates for surgery. By amplifying sound, these devices make up for the injured eardrum's reduced ability to transmit sound waves. Patients with hearing impairment can greatly improve their quality of life with the use of hearing aids.
Another important option is antibiotic therapy, especially when a persistent infection is the main issue. Antibiotics can help the eardrum's natural healing process and stop more damage by efficiently managing infections.
Homeopathic Treatments
By employing very diluted chemicals, homeopathy stimulates the body's natural healing processes, providing a supplementary method to treating diseases associated to the eardrum. Homeopathy can enhance general ear health and alleviate symptoms related to eardrum damage, but it cannot replace surgical intervention in extreme circumstances.
Several homeopathic remedies are commonly recommended for ear conditions:
1. Belladonna: Used for acute ear infections characterized by sudden onset, redness, heat, and throbbing pain. Belladonna is particularly effective in cases where symptoms develop rapidly.
2. Pulsatilla: Often prescribed for earaches with a sensation of fullness and mild infections, especially when associated with colds. Pulsatilla can also help alleviate ear discharge.
3. Hepar Sulphuris Calcareum: Suitable for sharp, splinter-like pain in the ear, particularly when the ear is sensitive to touch or cold air. This remedy is beneficial for infections with pus formation.
4. Silicea: Recommended for chronic ear infections with persistent discharge. Silicea is also used to support the expulsion of foreign bodies or debris from the ear.
5. Chamomilla: Effective for severe ear pain, especially in children who are irritable and restless. Chamomilla helps calm the patient and relieve pain.