Ear Drum Rupture and its Treatment
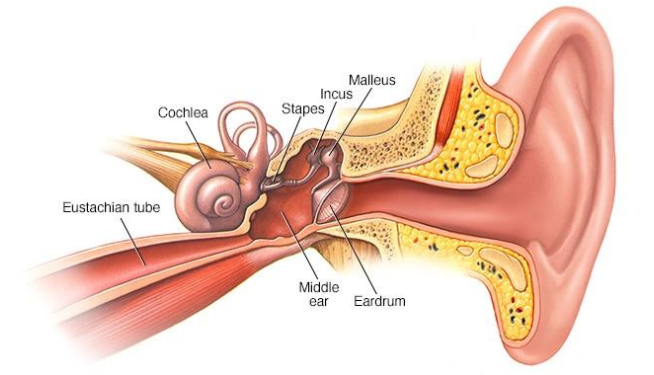
Ear Drum Rupture (Tympanic Membrane Perforation):
A ruptured eardrum occurs when there is a tear or hole in the thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear, known as the tympanic membrane. This condition can be painful and lead to various complications if not treated properly.
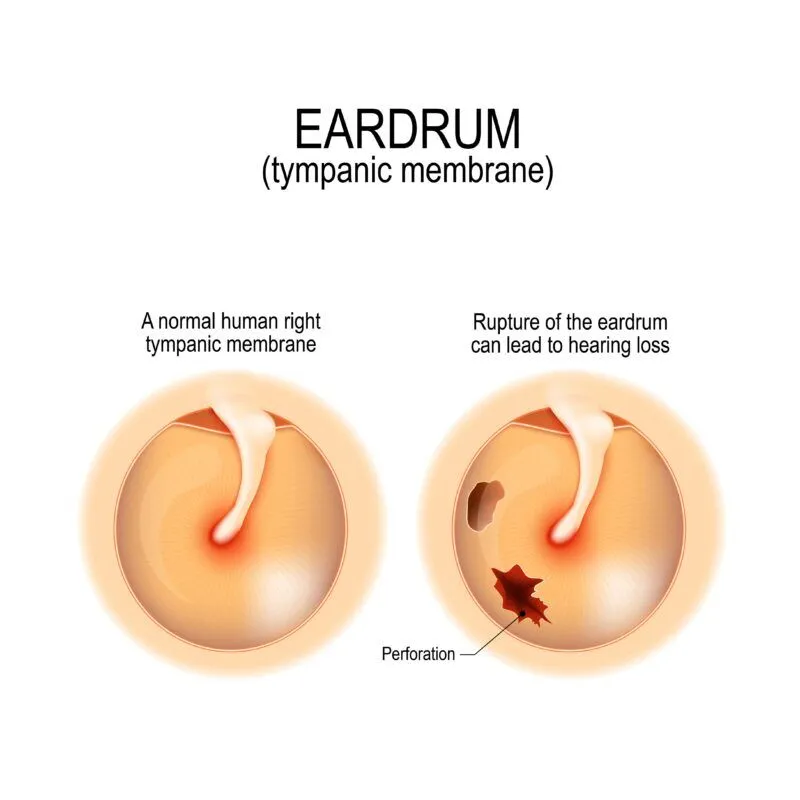
Causes of Ear Drum Rupture:
- Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Chronic middle ear infections can lead to pressure buildup in the middle ear, causing the eardrum to rupture.
- Trauma: Direct injury to the ear, such as from a blow, fall, or foreign object entering the ear (e.g., cotton swabs), can cause perforation.
- Sudden Pressure Changes: A sudden change in air pressure, such as during air travel or diving, can lead to a rupture, commonly referred to as barotrauma.
- Loud Noises (Acoustic Trauma): Exposure to very loud sounds or explosions can cause a rupture of the eardrum due to intense pressure.
- Water Exposure: Prolonged exposure to water, especially in cases of ear infections or damage, can lead to rupture.
- Inserting Objects into the Ear: Inserting cotton swabs, hairpins, or other objects into the ear canal can puncture the eardrum.
Symptoms of a Ruptured Eardrum:
- Pain: Sharp or sudden pain in the ear, which may be intense and throbbing at first, followed by a relief once the rupture occurs.
- Hearing Loss: Partial or complete loss of hearing in the affected ear.
- Ear Discharge (Otorrhea): Pus, blood, or clear fluid may drain from the ear, especially if an infection is present.
- Ringing in the Ear (Tinnitus): A ringing or buzzing sound in the ear, which can be persistent or intermittent.
- Dizziness: A feeling of vertigo or imbalance due to the disruption in the inner ear.
- Itching or Fluid in the Ear: Fluid buildup or a sensation of fullness in the ear.
Side Effects and Complications of a Ruptured Eardrum:
- Infections: If left untreated, a ruptured eardrum can lead to recurrent ear infections (chronic otitis media).
- Chronic Hearing Loss: In some cases, the rupture can cause long-term or permanent hearing impairment if the membrane does not heal properly.
- Tinnitus: Persistent ringing or buzzing in the ear can occur and may continue even after healing.
- Mastoiditis: A potentially serious infection that must be treated by a doctor that spreads to the mastoid process, the bones behind the ear.
- Cholesteatoma: A growth of skin cells behind the eardrum that can develop as a result of repeated infections or a ruptured eardrum, which may require surgery.
- Perforation Size and Healing Problems: Larger perforations may not heal on their own and might require surgical intervention, such as a tympanoplasty.
Homeopathic Treatment for Ear Drum Rupture:
Homeopathic medicines are selected to promote the body's self-healing processes, with an emphasis on the patient's symptoms, general health, and constitution. Some popular homeopathic treatments for ear drum rupture are listed below:
1. Belladonna
- Indication: Used for sudden, intense pain, often associated with inflammation or infection of the ear.
- Symptoms: Throbbing pain, redness, fever, sensitivity to touch, and sudden onset of symptoms.
- Use: Recommended when pain is sharp, violent, and accompanied by fever.
2. Hepar Sulphuris Calcareum
- Indication: For infections of the ears that have developed into a rupture, particularly when pus is being discharged.
- Symptoms: Intense throbbing pain, sensitivity to cold air, pus or yellowish discharge from the ear, and swelling.
- Use: Best for severe infections or cases where there is a tendency to develop abscesses.
3. Mercurius Solubilis
- Indication: Used for conditions involving ear discharge, especially if the discharge is thick, greenish, or foul-smelling.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include ear pain, thick or unpleasant discharge, enlarged glands, sensitivity to temperature changes, and symptoms that are worse at night.
- Use: Suitable when the rupture is associated with an ongoing infection and discharge.
4. Chamomilla
- Indication: For severe ear pain, often with irritability and restlessness, commonly used in children.
- Symptoms: Sensitivity, moodiness, restlessness, and a sharp, shooting pain in the ear.
- Use: Ideal when the pain is unbearable and the person is very sensitive to it.
5. Calcarea Carbonica
- Indication: Helpful for chronic or recurrent ear infections, especially when the rupture is due to a longstanding issue.
- Symptoms: Thick earwax, recurring infections, and a tendency to catch colds frequently.
- Use: Used for chronic cases or those prone to recurrent ear problems.
6. Arnica Montana
- Indication: Primarily used for trauma-induced ear ruptures (blows, pressure changes, accidents).
- Symptoms: Pain, bruising, and soreness following an injury, and a feeling of shock or fear.
- Use: Ideal for recovery after an injury or sudden trauma to the ear.