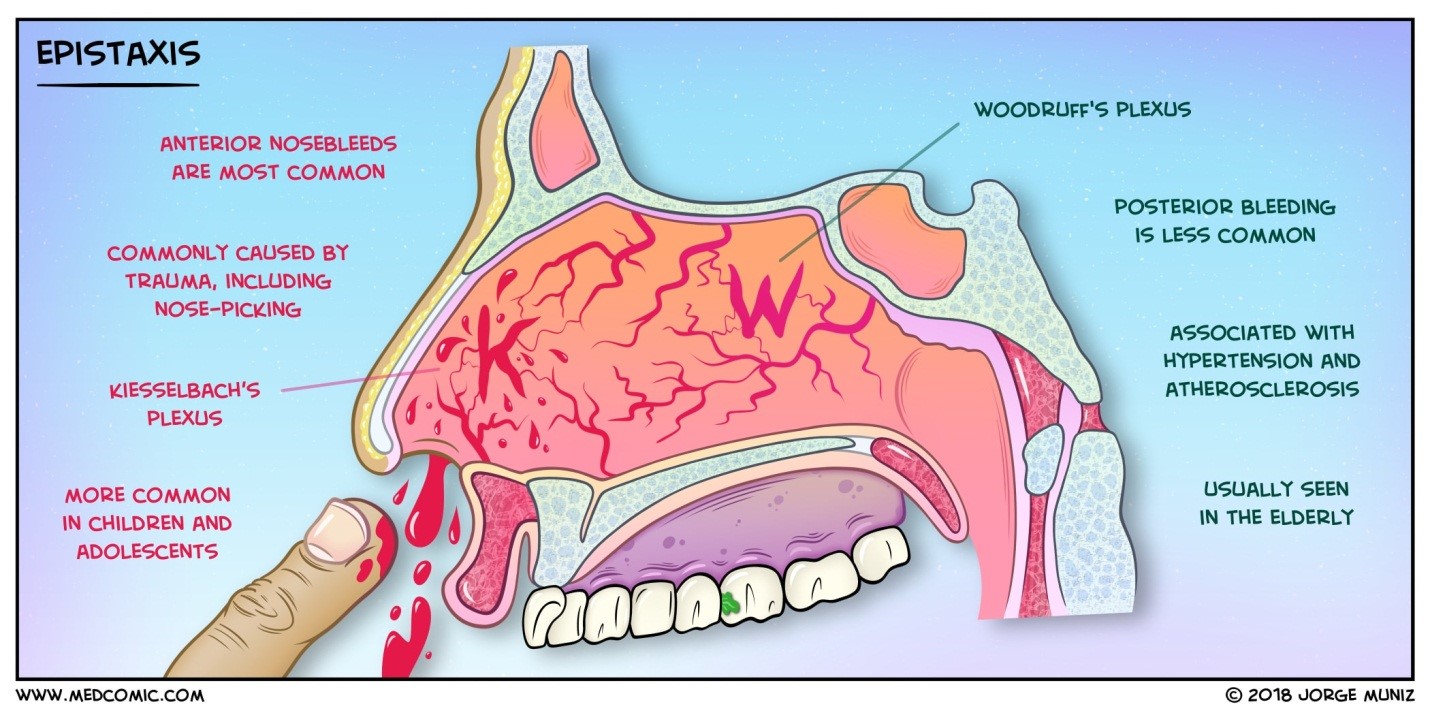
Epistaxis and Its cure in Homeopathy
Nosebleeds (likewise called epistaxis) can happen effectively in light of the area of the nose and the near the-surface area of veins in the coating of your nose. Most nosebleeds can be dealt with at home, however certain indications ought to be checked by a doctor.
What is a nosebleed?
Basically, a nosebleed is the deficiency of blood from the tissue that lines within your nose.
Nosebleeds (additionally called epistaxis) are normal. Some 60% of individuals will have somewhere around one nosebleed in the course of their life. The area of the nose in the face and the enormous number of veins near the surface in the covering of your nose make it an obvious objective for injury and nosebleeds.
Types of Nosebleeds:
Indeed. Nosebleeds are portrayed by the site of the drain. There are two principle types and one is more genuine than the other.
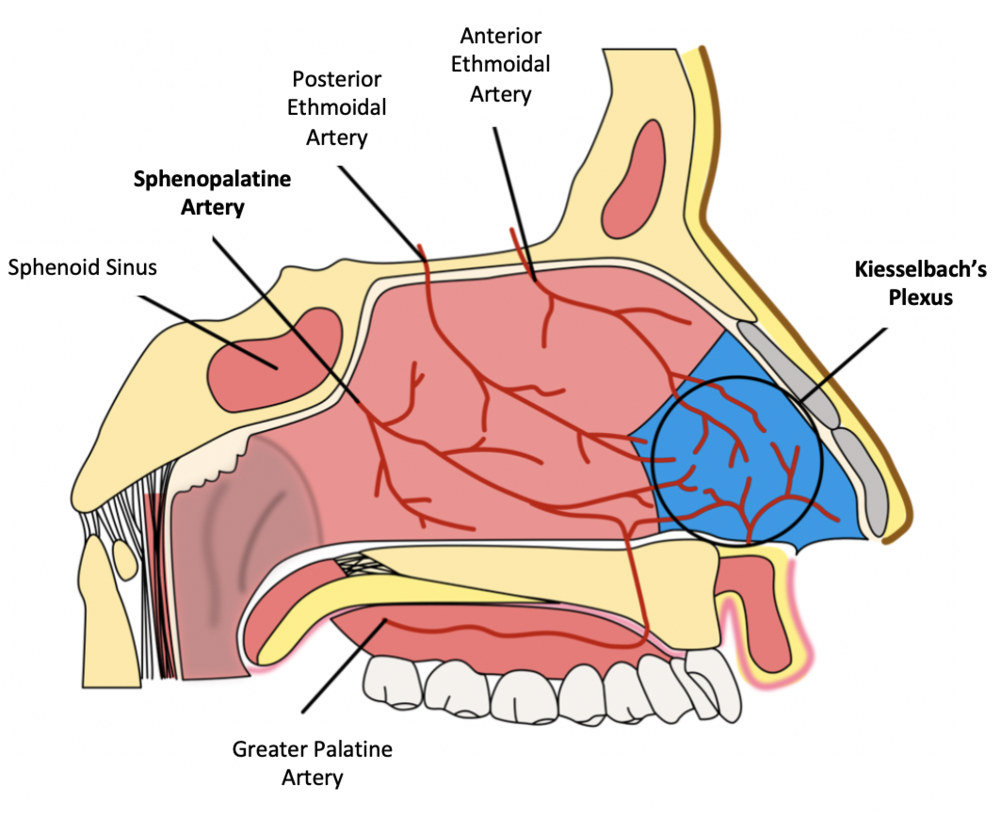
A foremost nosebleed begins toward the front of the nose on the lower part of the divider that isolates the different sides of the nose (called the septum). Vessels and little veins in this front space of the nose are delicate and can without much of a stretch break and drain. This is the most well-known kind of nosebleed and is generally not genuine. These nosebleeds are more normal in youngsters and are generally ready to be treated at home.
A back nosebleed happens somewhere inside the nose. This nosebleed is brought about by a drain in bigger veins in the back piece of the nose close to the throat. This can be a more genuine nosebleed than a front nosebleed. It can bring about weighty dying, which might stream down the rear of the throat. You might require clinical consideration immediately for this kind of nosebleed. This kind of nosebleed is more normal in grown-ups.
Who gets nosebleeds?
Anybody can get a nosebleed. The vast majority will have no less than one in the course of their life. Be that as it may, there are individuals who are bound to have a nosebleed. They include:
• Children between ages two and 10. Dry air, colds, hypersensitivities and staying fingers and items into their nose make kids more inclined to nosebleeds.
• Adults between ages 45 and 65. Blood might set aside more effort to cluster in midlife and more seasoned grown-ups. They are likewise bound to be taking blood diminishing medications, (for example, day by day headache medicine use), have hypertension, atherosclerosis (solidifying of the dividers of supply routes) or a draining issue.
• Pregnant ladies. Veins in the nose extend while pregnant, which squeezes the sensitive veins in the coating of the nose.
• People who take blood-diminishing medications like headache medicine or warfarin.
• People who have blood coagulating messes, like hemophilia or von Willebrand illness.
Side effects and Causes:
Nosebleeds have many causes. Luckily, most are not genuine.
The most widely recognized reason for nosebleeds is dry air. Dry air can be brought about by sweltering, low-moistness environments or warmed indoor air. The two conditions cause the nasal film (the sensitive tissue inside your nose) to dry out and become dry or broken and bound to drain when scoured or picked or when cleaning out your nose.
Other normal reasons for nosebleeds include:
• Nose picking.
• Colds (upper respiratory contaminations) and sinusitis, particularly scenes that cause continued wheezing, hacking and nose blowing.
• Blowing your nose with power.
• Inserting an item into your nose.
• Injury to the nose as well as face.
• Allergic and non-hypersensitive rhinitis (irritation of the nasal coating).
• Blood-diminishing medications (headache medicine, non-steroidal mitigating medications, warfarin, and others).
• Cocaine and different medications breathed in through the nose.
• Chemical aggravations (synthetic substances in cleaning supplies, compound vapor at the working environment, other solid scents).
• High heights. The air is more slender (absence of oxygen) and drier as the height increments.
• Deviated septum (an unusual state of the divider that isolates the different sides of the nose).
• Frequent utilization of nasal splashes and drugs to treat irritated, runny or stodgy nose. These prescriptions – antihistamines and decongestants – can dry out the nasal layers.
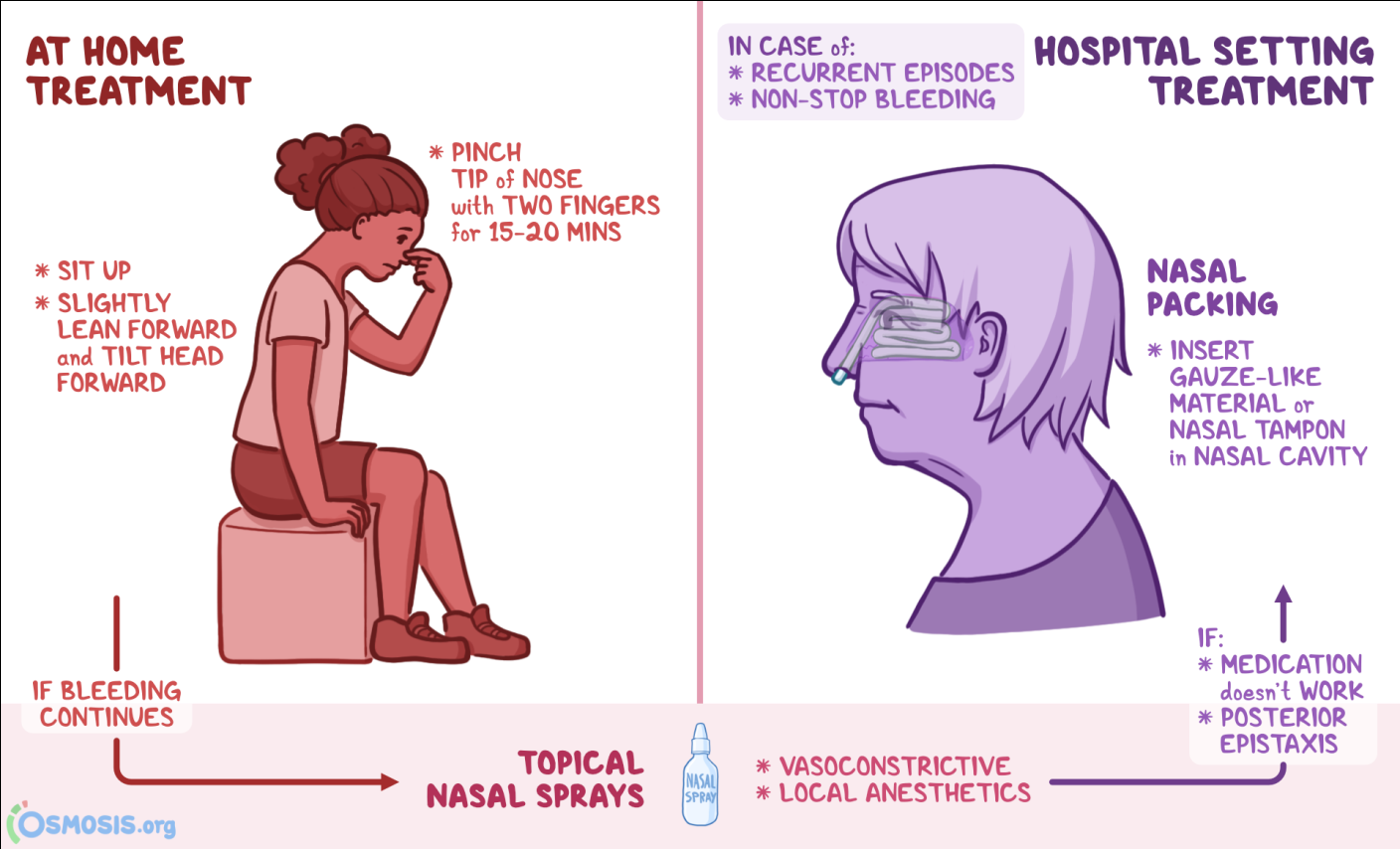
Homeopathic Medicine for Epistaxis:
Hamamelis:
Hamamelis is an excellent enemy of hemorrhagic medication for epistaxis. It functions admirably for draining from different holes of the body, including nasal dying. Hamamelis offers a great deal of help in epistaxis when the blood is dull and incoagulable. Alongside nasal dying, there is an irritation in the nose.

Phosphorus:
Phosphorus is among the best prescriptions to control draining from different body parts. It is a similarly successful enemy of hemorrhagic cure as Hamamelis. Phosphorus is recommended for dazzling red nasal dying. Phosphorus helps in diminishing the inclination towards intermittent epistaxis scenes.

Crocus Sativus:
Crocus Sativus is one more exceptionally successful medication for epistaxis with dull or dark, wiry nasal dying. Crocus Sativus functions admirably in epistaxis where the nasal blood is dull or dark with viscid strings that hang down the nose as string or rope. Alongside nasal dying, there is outrageous actual shortcoming and exhaustion.

Arnica:
Arnica is a profoundly dependable and proficient treatment for epistaxis brought about by a physical issue. Arnica, otherwise called Leopard's Bane, is a characteristic medication for instances of injury. It is an enemy of injury cure found in the medical aid packs, everything being equal. Aside from epistaxis because of injury, Arnica is likewise suggested for nasal draining during typhoid fever.

Regard: Dr. Naveed Shahzad