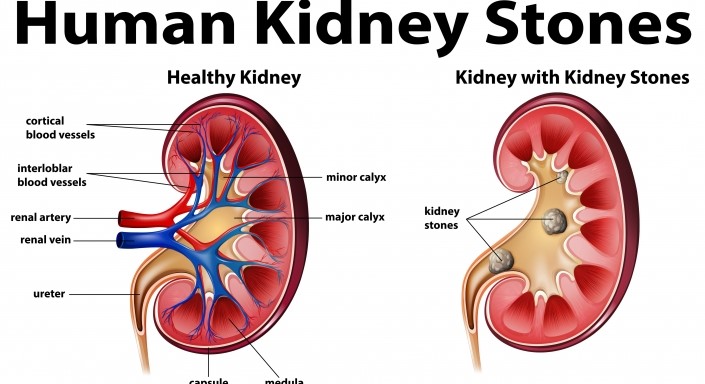
Kidney Stones and Its cure in Homeopathy
Kidney stones, or renal calculi, are strong masses made of gems. Kidney stones normally start in your kidneys.
• Kidneys
• Ureters
• Bladder
• Urethra
Kidney stones are quite possibly the most ridiculously excruciating ailments. The reasons for kidney stones change as indicated by the sort of stone.
Kinds of kidney stones:
Not all kidney stones are comprised of similar gems.
Calcium:
Calcium stones are the most widely recognized. Eating less oxalate-rich food sources can diminish your danger of fostering this kind of stone. High-oxalate food sources include:
• Potato chips
• Peanuts
• Chocolate
• Beets
• Spinach
Nonetheless, despite the fact that some kidney stones are made of calcium, getting sufficient calcium in your eating routine can keep stones from shaping.
Uric Corrosive:
This kind of kidney stone is more normal in men than in ladies. They can happen in individuals with gout or those going through chemotherapy.
This kind of stone creates when pee is excessively acidic. An eating regimen wealthy in purines can expand pee's acidic level. Purine is a drab substance in creature proteins, like fish, shellfish, and meats.
Struvite:
This kind of stone is discovered for the most part in ladies with urinary plot contaminations (UTIs). These stones can be enormous and cause urinary impediment. They result from a kidney disease. Treating a basic contamination can forestall the improvement of struvite stones.
Cystine:
Cystine stones are uncommon. They happen in all kinds of people who have the hereditary issue cystinuria. With this kind of stone, cystine — a corrosive that happens normally in the body — spills from the kidneys into the pee.
Hazard Factors for Kidney Stones:
The most serious danger factor for kidney stones is making under 1 liter of pee each day. This is the reason kidney stones are normal in untimely newborn children who have kidney issues. Notwithstanding, kidney stones are probably going to happen in individuals between the ages of 20 and 50. A background marked by kidney stones can expand your danger. So does a family background of kidney stones.
Other danger factors include:
• Dehydration
• Obesity
• A diet with significant degrees of protein, salt, or glucose
• Hyper parathyroid condition
• Gastric sidestep a medical procedure
• Inflammatory entrail illnesses that increment calcium retention
• taking meds, for example, triamterene diuretics, antiseizure medications, and calcium-based acid neutralizers
Side Effects of a Kidney Stone:
Kidney stones are known to cause extreme torment. Manifestations of kidney stones may not happen until the stone starts to drop down the ureters. This serious aggravation is called renal colic. You might have torment on one side of your back or midsection.
In men, torment might emanate to the crotch region. The aggravation of renal colic goes back and forth, however can be extreme. Individuals with renal colic will in general be fretful.
Different indications of kidney stones can include:
• Blood in the pee (red, pink, or earthy colored pee)
• vomiting
• Nausea
• Discolored or putrid pee
• chills
• Fever
• Frequent need to pee
• Urinating modest quantities of pee
On account of a little kidney stone, you might not have any aggravation or indications as the stone goes through your urinary plot.
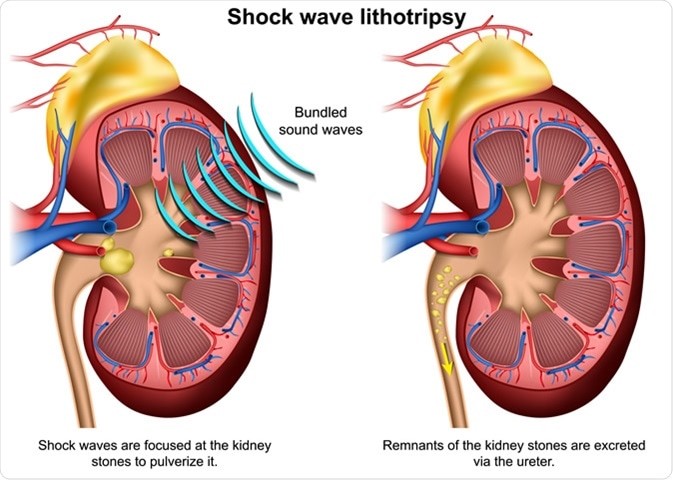
Why kidney stones can be an issue?
Stones don't generally remain in the kidney. In some cases they pass from the kidney into the ureters. Ureters are little and fragile, and the stones might be too huge to even think about passing flawlessly down the ureter to the bladder.
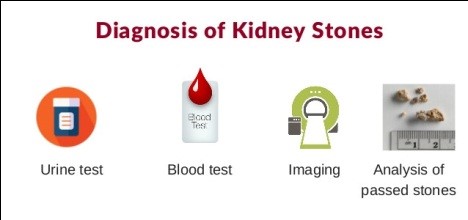
Testing For and Diagnosing Kidney Stones:
Analysis of kidney stones requires a total wellbeing history evaluation and an actual test. Different tests include:
• Blood tests for calcium, phosphorus, uric corrosive, and electrolytes
• Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine to survey kidney working
• Urinalysis to check for gems, microorganisms, blood, and white cells
• Examination of passed stones to decide their sort
The accompanying tests can preclude obstacle:
• Abdominal X-beams
• Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
• Retrograde pyelogram
• Ultrasound of the kidney (the favored test)
• MRI output of the mid-region and kidneys
• Abdominal CT filter
Medicine for Kidney Stone
Sarsaparilla:
Passage of rock or little calculi; RENAL colic; STONE in bladder; bleeding pee. Pee: splendid and clear however aggravating; inadequate, foul, flaky, sandy, abundant, passed without sensation; stores white sand.
Nux-V:
RENAL colic is brought about by a STONE in the ureter, which by its aggravation causes a fitful grasping of the roundabout strands of that channel; the appropriate medication loosens up these filaments and the pressing factor from behind powers the calculi out immediately.

Cantharis:
Constant and unbearable asking to pee previously, during and after pee. Consuming, burning pee, with cutting, grievous asking, and unfortunate tenesmus or spilling stranguary. Pee is passed drop by drop. Unbearable asking with tenesmus. Pee burns the entry. Jam like shreddy pee.

Berberis Vulgaris:
Painful cuttings left side bladder into the urethra, comes from the left kidney (proceeded with) the course of the ureter. Dark red pee, expediently becomes turbid, stores thick, coarse, dazzling red residue, gradually turning out to be clear, yet continually holding its blood.

Regard: Dr. Naveed Shahzad