Hypermetropia and Its cure in Homeopathy
where equal beams of light coming from endlessness are shone behind the light touchy layer of the retina, when the eye is very still.
Donders (1864) examines in his authentic audit about hypermetropia. A large part of the issue was created by turmoil between the impacts of presbyopia and hypermetropia on close to vision.
Little hypermetropia might be revised by deliberate convenience. Indeed, even high mistakes of refraction might be remedied along these lines, however raised glasses might be required in case indications are not eased.
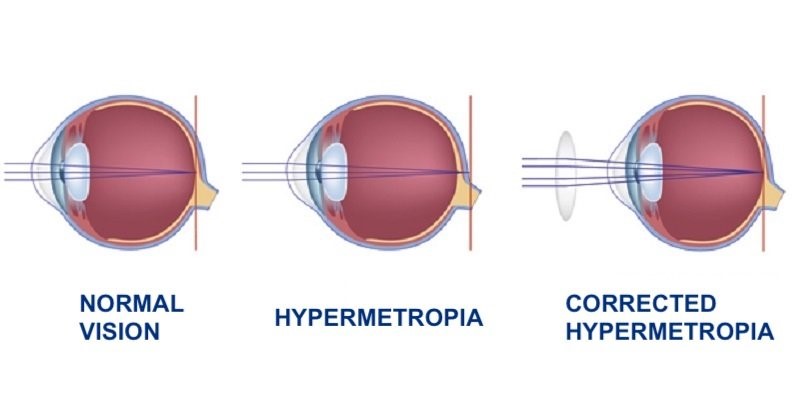
Refractive mistake (ametropia) results when cornea and focal point deficiently shine the light beams, bringing about obscured pictures. The estimating unit for refractive blunder is dioptre (D), which is characterized as the corresponding of the central length in meters.
In this way, the pictures don't center when they reach to the retina. For clear vision, a hypermetropic eye should oblige to expand its lenticular ability to get far off objects center around retina. This requires withdrawal of ciliary muscle, and hence, far-located eye is rarely very still and work significantly harder to see close to objects obviously. Hypermetropic amendments add positive centering capacity to the eye for clear vision.
Manifestations:
The manifestations fluctuate contingent on the age of the patient and the seriousness of refractive mistake. Patient might be asymptomatic. Modest quantity of refractive mistake in youthful patients is normally adjusted by gentle accommodative exertion, without creating any indications.
Indicative patients might give:
At the point when hypermetropia is completely amended: At times the hypermetropia is completely rectified (in this manner vision is typical) yet because of supported accommodative endeavors the patient creates asthenopic side effects.
• Asthenopia (eye fatigue).
• Frontal or fronto-worldly migraine.
• Watering.
• Mild antipathy for light.

These manifestations deteriorate as the day advances and are irritated by delayed close to work. At the point when hypermetropia isn't completely amended: When hypermetropia isn't completely adjusted by the deliberate accommodative endeavors, then, at that point the patient grumbles of deficient vision more for close than distance, because of supported accommodative exertion. Patient present with:
• Defective vision more for close.
At the point when hypermetropia is high: When hypermetropia is high (multiple D), the patients normally don't oblige and they endure with:
• Marked blemished vision for both close and distance.
• Blurring of vision at a more youthful age than in emmetrope.
When there is Spasm of convenience: Spasm of convenience might initiate pseudo-nearsightedness. It could be distinguished by cycloplegic refraction. It presents as:
• Intermittent unexpected obscuring of vision.
As a rule, youngster may likewise give cover infections (like blepharitis, eye blister or chalazion), united squint or amblyopia.

Causes:
Hypermetropia might be:
• The absolute refractive force of the eye is typical however there is pivotal shortening of the eyeball.
• Curvature hypermetropia: Curvature hypermetropia is that condition wherein ebb and flow of the cornea, focal point or both is expanded (compliment) than the typical, bringing about change in refractive force of the eye. Around 1 mm expansion in span of ebb and flow brings about 6 D of hypermetropia.
• Index Hypermetropia: Index Hypermetropia happens because of progress in refractive list of the glasslike focal point with age.
• Positional hypermetropia: Positional hypermetropia results from posteriorly positioned translucent focal point of the eye.
• Absence of translucent focal point: Absence of glasslike focal point either inborn nonappearance or obtained (following careful evacuation or back dislodging) prompts aphakia. There is high hypermetropia in aphakia.

Analysis
Analysis of hypermetropia depends on the side effects and clinical signs noticed.
Clinical signs:
Visual sharpness:
Visual keenness changes with level of hypermetropia and force of convenience. Patients with low level of refractive blunder might have ordinary visual keenness. Nonetheless, there is decline in visual keenness for seeing close to objects.
Eyelids:
One might foster blepharitis, eye blister or chalazion. The relationship between's cover conditions and hypermetropia isn't clear.
Eyeball:
Size of the eyeball might be typical or little.
Cornea:
Cornea may likewise be marginally more modest in size. There might be related state of cornea plana (level cornea).
Lens:
Lens might be separated in reverse.

Hypermetropia Homeopathic Medicine:
Argentums Nitricum:
Argentums Nitricum is helpful in reestablishing capacity to debilitated ciliary muscles. Throbbing and tired inclination in the eyes, better by squeezing or shutting them. Eye strain creates because of sewing and working in a warm room.

Calcarea Carbonica:
Calcarea carbonica is simple exhaustion of the eyes and obscurity of vision, as though glancing through a fog, by consistent perusing and composing. Lachrymation promptly toward the beginning of the day and the patient is touchy to light. Far located.

Carbo Animalis:
Objects appear to be distant and there is obscurity if vision when perusing, better scouring the eyes. Helpful un feeble waterfall. Sensation as though something lay over the eyes. In this manner thinks that it is hard to gaze upward. The patient is extremely frail and unavoidably exceptionally crippled.

China Officinalis:
eyes are difficult while perusing and composing. Pressing factor in the eyes. As though from tiredness. Contortion of eyeballs. Pallor of the retina causing night visual impairment. Frequently, there is ciliary neuralgia.

Regard: Dr. Naveed Shahzad