Diabetes and Its Treatment
Diabetes & Controlling Method's for Diabetes
Diabetes is a type of disease for the group of blood, that affects how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is essential for your health because it is a crucial source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. It is your primary source of brain fuel.
The root cause of diabetes varies by type. But, no matter what kind of diabetes you have, it can cause high blood sugar. If your blood sugar leads to high regularly, it means you have diabetes, and it is not suitable for health.
Chronic diabetic conditions include the name of reversible diabetes calls diabetes. Reversible diabetes conditions have prediabetes and gestational diabetes ( sub-two types for diabetes). Prediabetes occurs when your blood sugar level is higher than usual, but it is not enough to classify it as diabetes. And prediabetes is often a precursor to diabetes is only done when we recruit perfect solution and treatment are taken to stop the progression. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy but can resolve after childbirth.
Diabetes symptoms depend on how high your blood sugar is. Some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2- diabetes, may not experience symptoms at all. In type 1 diabetes, the signs come on quickly and become more severe.
Necessary Indication for the Diabetes
- Increasing of thirst although drink plenty of water daily
- Urination system is in speed up.
- High appetite and feeling fatigue
- Losing weight in a remarkable manner
- Presentation of ketones (ketones are a by-product of muscle and fat breakdown, occurring when insulin is not available)
- Fatigue and stress to feeling all over the body
- Irritated
- Blurred vision or weak eye-sight vision
- The slow healing process and high blood flow during injury
- Recurrent infections such as gum or skin diseases and vaginal infections
- Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, although it is most often seen in childhood or adolescence. Type 2 diabetes, the most common type, can develop at any age, although it is more common in people over 40 years of age.
Try to Understand:
Now the next section is for the causes and the necessary info about the diabetes disease, but first, we go for it. We must understand some of the team and the working area's which mostly we use for the diabetes patient. Now let's have a look at this section which make you understand how it works for the patient of diabetes.
Working of Insulin in a body
It is a kind of hormone which is used for maintaining the glucose level in our body. It is coming for the gland which is situated in over body stomach it is behind and below near the pancreas. Now simply this insulin makes and develop the pancreas secretes into the stream of blood when it circulates in all over the body to enable the little sugar to be entered in your body.
When insulin injected in our body for the decreasing level of sugar, it ultimately lowers the amount of sugar. It means that when insulin makes in the body, your sugar level will be drop, so does the secretion of insulin done from the pancreas.
What is the Role of Glucose in a Body
Glucose is the name of sugar, or you can say that source of energy for the cells, which makes contact with body tissues. In simple words, the body cells which make up the muscles and tissue is called glucose. Now there are two essential terms from which we obtain the glucose:
- By food
- By liver process
It is naturally observed in the bloodstream where it to be entered by the help of insulin. The reason is that you cannot create or increase its level your own. You can improve it with some remedies and make the vitamin and protein in proper. But it is not much easy to have sugar level, and you have to increase it. Now if we move for the working of the liver, then we can say that it stores and make the glucose.
That's why one your glucose level kept slow it is because you can't eat anything. When you do that liver breaks down stored of glycogen into glucose and in the result, your sugar level control and stop to normal range.
Now here we Classified the Diabetes or sugar into two subparts which are as vital as the topic of sugar. Following are the Subtypes of these sugar disease and further formalities are also below on the page.
Major Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes which increases the sugar level as we mentioned before. A hormone called insulin transfers blood sugar to your cells, which is stored or used for energy. With diabetes, your body does not make enough insulin or use insulin effectively.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system attacks and destroys cells of the pancreas that helps to protect and regenerate or produce insulin. However, It is unknown at this Time what caused the fire and by the home to me has. It occurs in about 10% of people with this type of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes occurs when your body becomes resistant to insulin, and your blood sugar rises.
Prediabetes occurs when your blood sugar is higher than usual but not as high as those with type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar is elevated during pregnancy. The insulin-blocking hormone form and make the place by the placenta causes this type of diabetes. The rare condition known as diabetes insipidus is not related to diabetes mellitus, although it has a similar name. This is another condition in which your kidneys drain more fluid from your body.
Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. What is known is that your immune system - which usually fights harmful bacteria or viruses - attacks and destroys the cells that produce your insulin in the pancreas. It gives you less or no insulin. Instead of being carried into your cells, sugar rises in your bloodstream. Type 1 is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, although those factors are still unclear. It is not considered a weight factor of type 1 diabetes.
Sign for Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes may include:
- High appetite
- Increased thirst
- Lose weight accidentally
- Frequent urination
- Appearing cloudy
- Fatigue
- It can also cause a change in mood.
- Medication for Type 1 Diabetes
Additional medications for Type 1 Diabetes
High blood pressure medications: Your doctor may advise the test of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors to help keep your kidneys healthy. These medications are recommended for people with diabetes who have blood pressure greater than 140/90 mm Hg (mm Hg).
Aspirin: Your doctor may advise you to take a baby or regular aspirin daily to protect your heart.
Cholesterol-lowering drugs: Cholesterol guidelines are more aggressive for people with diabetes because of their lower risk of heart disease. The American Diabetes Association recommends that low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or "bad") cholesterol be less than 100 mg / dL (2.6 mmol / L). Your high-density lipoprotein (HDL, or "good") cholesterol is recommended to exceed 50 mg / dL (1.3 mmol / L) in women and 40 mg / dL (1 mmol / L) in men. Triglycerides, another type of blood fat, are ideal when they are less than 150 mg / dL (1.7 mmol / L).
Protective Life Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Careful management of type 1 diabetes can reduce your risk of serious - fatal - complications. Check out these tips:
Commit to managing your diabetes: Take your medication as needed. Tell all of you about type 1 diabetes. Make a healthy diet and exercise a part of your daily routine. Establish a relationship with a diabetes teacher and ask your health care team for help.
Identify yourself: Wear a tag or bracelet that use as an indication or sign which says you have diabetes. Keep a glucagon kit nearby if your blood sugar is low - and let your friends and loved ones know how to use it.
You have to make an annual physical exam and regular eye exams: Your regular diabetes checkup does not mean changing the physical yearly or regular eye exams. During physical activity, your doctor will look for a screen for diabetes-related problems as well as other medical issues. Your eye care specialist has to check for signs of retinal damage, cataracts monthly in case of type 1 diabetes.
Keep your immune system fresh: High blood sugar makes your immune system weak. The flu shot every year. Your doctor may also recommend a pneumonia vaccine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that you be vaccinated against hepatitis B if you have not previously been vaccinated against hepatitis B and if you are 19 to 59 years of age with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The CDC recommends vaccination as soon as possible after being diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. If you are 60 or older, and have diabetes and have not already been vaccinated, talk to your doctor if it is right for you.
Take care of your feet: Wash your feet daily in lukewarm water. Dry them gently, especially between the toes. Moisturize your feet with Ion Shadam. Check your feet daily for blisters, cuts, bruises, redness or swelling. Consult your doctor if you have a sore or other foot problem that is not cured.
Control your blood pressure and cholesterol: Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly can go a long way in controlling high blood pressure and cholesterol. Medications may also be required.
If you smoke or use other types of tobacco, ask your doctor for help: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes complications which including heart attack, stroke, and may nerve damage as well as kidney disease. Talk to your doctor about quitting smoking or quitting other types of tobacco.
If you drink alcohol, do it responsibly: Alcohol causes you to have high or low blood sugar, depending on how much you drink and at the same Time what you eat. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation and always with food. Check your blood sugar level before going to sleep.
Take stress seriously: The production of hormones in your body in response to prolonged stress can prevent insulin from working correctly, which can put you under more pressure. Take a step back and set some boundaries. Prioritize your tasks. Learn relaxation techniques. Get plenty of sleep.
Risky Factors: for Type 1 Diabetes
Although the exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not known, the risk factors for the increased risk are:
Family history: If your parents or siblings have type 1 diabetes, your risk increases.
Environmental factors: The chances of contracting a viral disease play some role in type 1 diabetes. Presence of harmful immune system cells (autoantibodies). Family members of people with type 1 diabetes are sometimes tested for the presence of diabetic autoantibodies. If you have these autoantibodies, you are at risk of developing type 1 diabetes. But not everyone with these auto-in bodies gets diabetes.
Geography: Some countries, such as Finland and Sweden, have a high rate of type 1 diabetes.
Complication's for Type 1 Diabetes:
Chronic complications of diabetes develop slowly. The longer you have diabetes - and the lower your blood sugar controls - the higher the risk of complications. Eventually, diabetes complications will stop or become fatal. Possible issues:
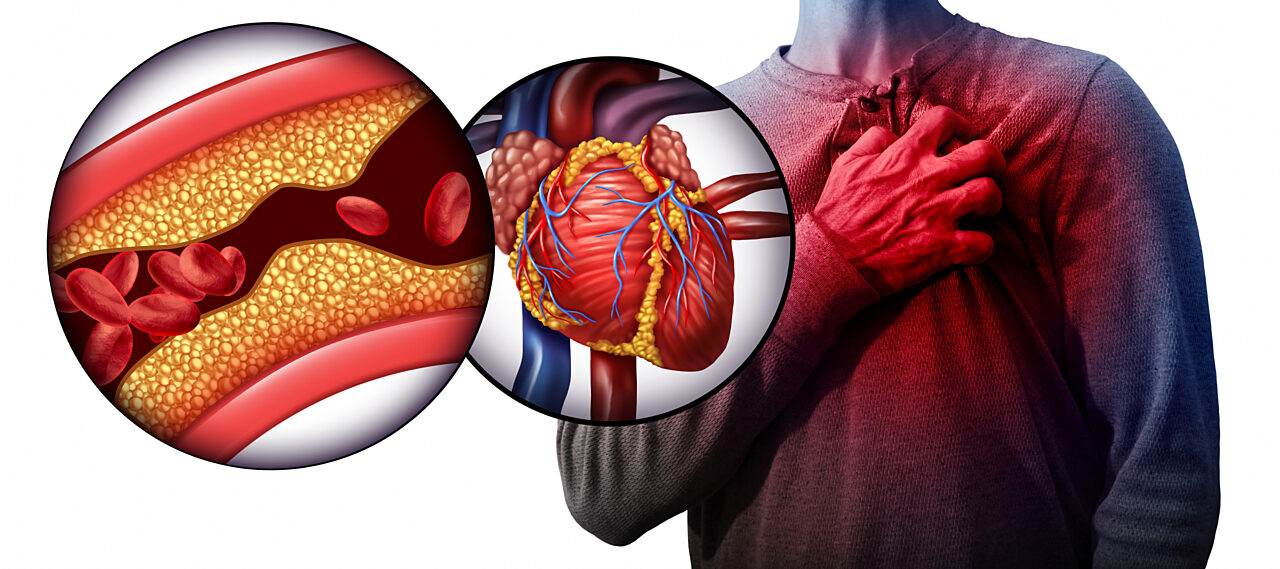
Heart disease: Diabetes increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including chest pain (angina) with coronary artery disease, heart attack, atherosclerosis and atherosclerosis). If you have diabetes, then solid chances may you have heat stroke just because of this diabetes?
Nerve damage (neuropathy): Excess sugar can damage the walls of the small blood vessels (capillaries) that feed your veins, especially in your feet. It usually starts on the toes or fingers and causes tingling, numbness, burning or pain that gradually spreads upwards.
If left untreated, you may lose all sensation in the affected limbs. Damage to the nerves related to digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation. For men, it can be erectile dysfunction.
Kidney damage (nephropathy): The kidneys have millions of small blood vessels (glomeruli) that filter waste from your blood. Diabetes damages this delicate filtering system. Severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
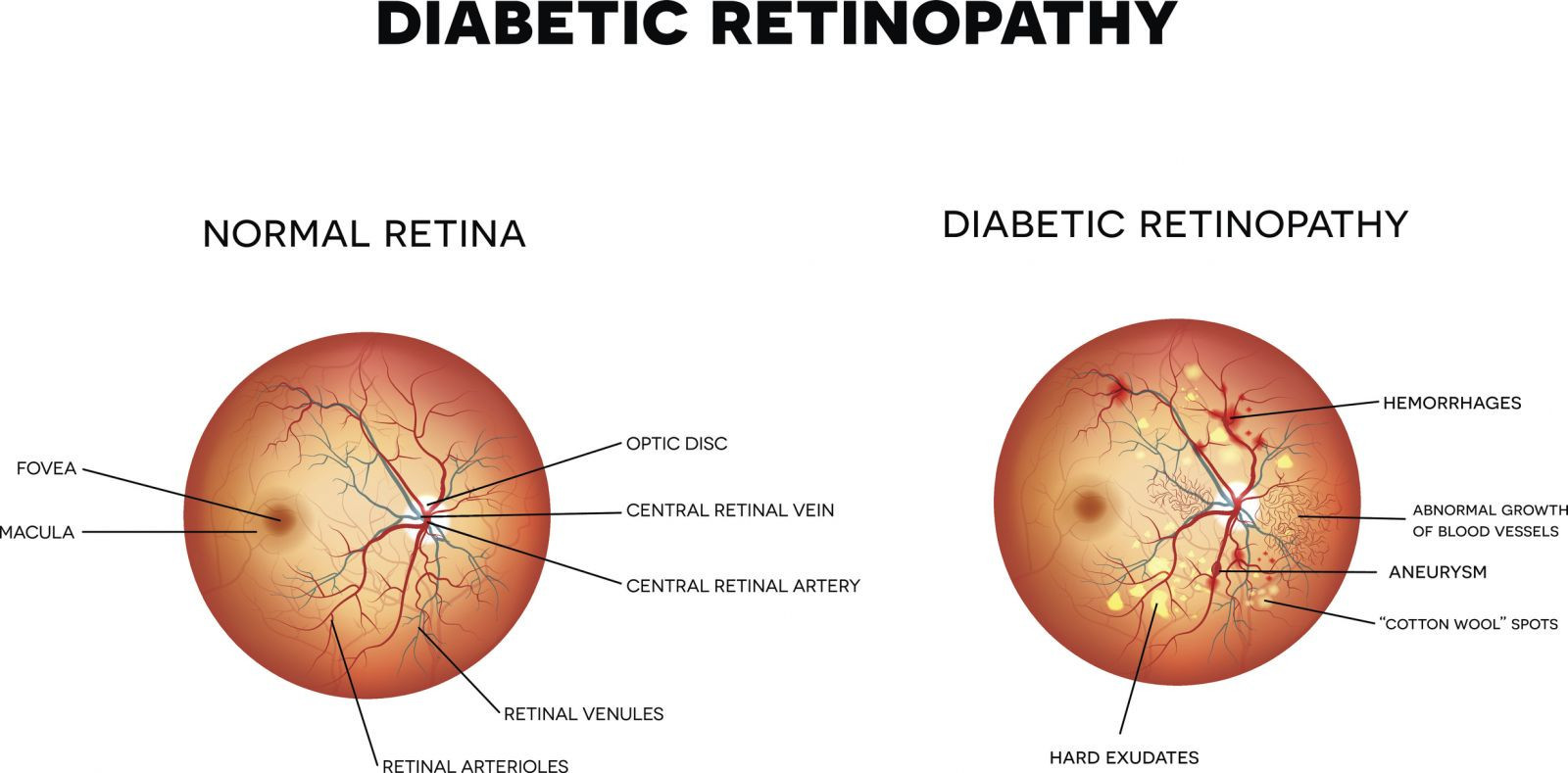
Damage to the eye (retinopathy): Diabetes damages the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), which can lead to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other severe vision conditions such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Damage to the feet: Damage to the nerves in the feet or lack of blood to the feet increases the risk of various problems of the feet. If left untreated, cuts and blisters can cause serious infections, which often lead to proper treatment. These infections may eventually require amputation of the leg, foot or ankle.
Skin condition: Diabetes is more likely to cause skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.
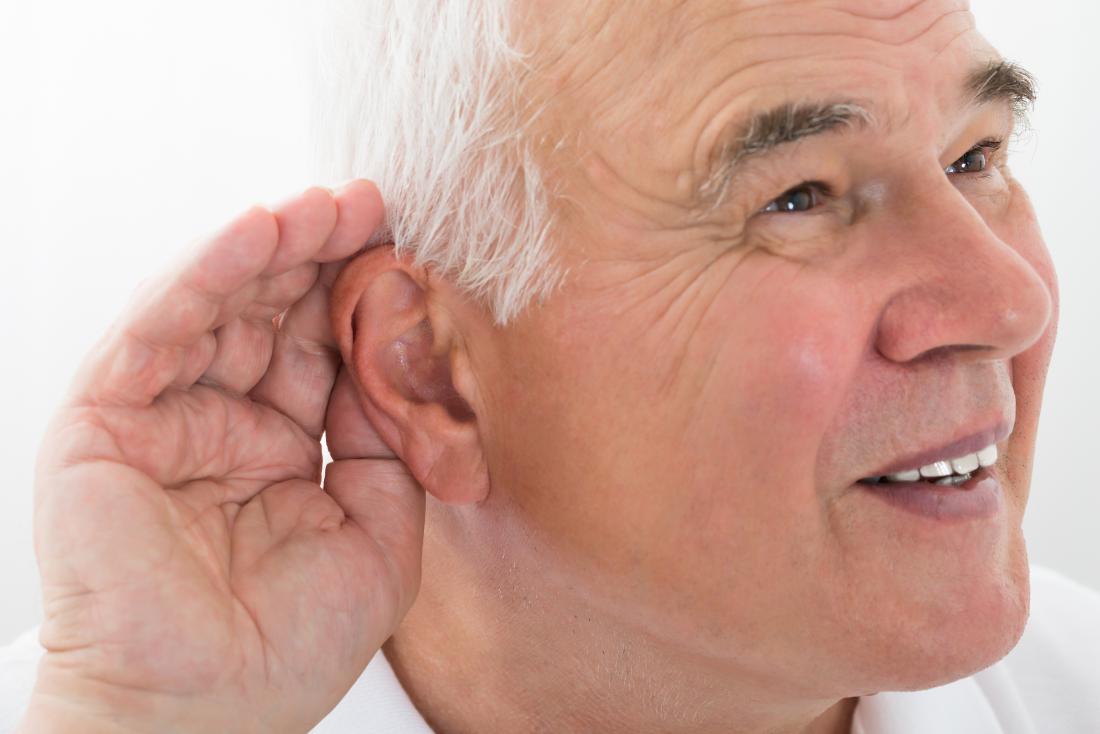
Deaf: Hearing problems are more common in people with diabetes.
Alzheimer's disease: Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease. If your blood sugar control is lacking, the risk is high. Despite such differences in how to exacerbate these disorders, nothing has been proven.
Prevention for Type 1 Diseases:
Type 1 diabetes cannot be stopped. However, the same healthy lifestyle options that help treat prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes can also help prevent them:
Eat a healthy diet: Choosing foods is harmful to you that is low in fat and calories and high in fibre because it causes the sugar to a high level. Focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Try to diversify to avoid boredom.
Do more physical activity: Aim for about 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise on most days of the week or at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week. Lose extra pounds If you are overweight, you are also losing 7% of your body weight - for example, if you weigh 200 pounds (90.7 kg) 14 pounds (6.4 kg) - reduces the risk of diabetes. However, do not try to lose weight during pregnancy. Talk to your doctor about how much you weigh during pregnancy.
Focus on permanent changes in your diet and exercise habits to keep your weight in a healthy range. Motivate yourself by remembering the benefits of weight loss, such as a healthy heart, more energy and better self-esteem. Sometimes medications are also an option. Oral diabetes medications such as metformin (Glumetza, Fortamet, et al.) reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes - but healthy lifestyle choices are essential. Check your blood sugar at least once a year to see if you have developed type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented because immune system problems cause it. Some causes of type 2 diabetes, such as your genes or age, are out of your control. Yet many other diabetes risk factors are controlled. Most diabetes prevention strategies include simple adjustments in your diet and fitness routine.
If you are already diagnosed with diabetes, here are some things you can do to delay or prevent type 2 diabetes:
- Get at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise a week, such as walking or cycling.
- From your diet, cut out saturated and trans fats with refined carbohydrates.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Eat small portions.
- If you are overweight or have ese arrears, try to lose 7 per cent of your body weight.
- These are not the only ways to prevent diabetes. Find out more strategies that can help you avoid this chronic disease.
Type 1 Diabetes in Children:
This type of diabetes is the general form of diabetes often begins in childhood. Increased urination is one of the main symptoms. Children with type 1 diabetes can start bedwetting after toilet training. Excessive thirst, fatigue, and hunger are also signs of this condition. It is essential to treat children with type 1 diabetes immediately. The disease causes high blood sugar and dehydration, which is a medical emergency.
Type 2 Diabetes
Eating the right kind of food can help control your blood sugar and reduce excess weight. The carb count is an essential component of eating type 2 diabetes. Dietitians can help you figure out how many grams of carbohydrate you eat at each meal.
To keep your blood sugar levels regular as well as stable, you must eat small meals throughout the day after a break of every three to four hours. Emphasize healthy eating:
- Fruit
- Vegetables
- Cereals
- Lean proteins like chicken and fish
- Healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts
- Some other foods can weaken your blood sugar control efforts. If you have diabetes, you should avoid those foods.
Diagnoses of Diabetes
Anyone with symptoms of diabetes or at risk for the disease should be tested. On the second or third Time of pregnancy, women are regularly tested for gestational diabetes.
Doctors diagnose prediabetes and diabetes using these blood tests:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) test measures your blood sugar 8 hours after fasting.
- The A1C test provides a snapshot of your blood sugar levels over the past three months.
- To diagnose gestational diabetes, your doctor will test your blood sugar levels between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- During a glucose challenge test, your blood sugar is checked one hour after drinking the sugar liquid.
- A 3-hour glucose tolerance test tests your blood sugar after fasting overnight and drinking sugar.
Treatment for type 2 diabetes includes:
- Insulin intake
- Carbohydrate, fat and protein count
- Frequent blood sugar monitoring
- Eating a healthy diet.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight
The goal is to keep your blood sugar level as close as possible or to prevent problems. Generally, the goal is to maintain your daytime blood sugar level between 80 and 130 mg / dL (4.44 to 7.2 mmol / L) and 180 mg / dL (10 mmol / L) after your meal. L) Do not exceed two hours after eating.
Symptoms for Type 2 Diabetes
Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes create very slowly. You may have type 2 diabetes and not know it. Search:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Appetite increases
- Sudden weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing
- Recurrent infection
- Darker skin areas, usually on the armpits and neck
Risky Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Factors that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes:
Weight: It is narrated that overweight is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Fat distribution: If you store mainly belly fat, you have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than if you store fat elsewhere, such as your hips and thighs. If you are a man with a waist circumference of over 40 inches (101.6 cm) or a woman with a waist circumference of 35 inches (88.9 cm), you are at risk for type 2 diabetes.
Inactivity: If you are less active, your risk of type 2 diabetes is higher. Physical activity helps you control your weight, uses glucose as energy, and makes your cells more sensitive to insulin.
Family history: If your parents or siblings have type 2 diabetes, the risk of type 2 diabetes increases.
Race or ethnicity: While this is not clear, some - including black, Hispanic, American Indian, and Asian American people - are at greater risk.
Ages: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as you get older, especially after the age of 45. This is because people exercise less, lose muscle weight, and gain weight as they age. But type 2 diabetes is also on the rise in children, adolescents, and young adults.
Prediabetes: Prediabetes is when your blood sugar level is higher than normal, but it is not enough to classify it as diabetes. If left untreated, prediabetes often progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes: If you develop gestational diabetes while you are pregnant, your risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases. If you give birth to a baby who weighs more than 9 pounds (4 kg), you are also at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Polycystic ovary syndrome: For women, having polycystic ovarian syndrome - a common condition such as irregular structure, excessive hair growth, and esophagus - increases the risk of diabetes.
Diagnoses Test for Type 2 Diabetes
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level over the last two to three months. The normal level is less than 5.7 percent, and results between 5.7 and 6.4 percent are considered prebiotic. Having A1C levels of 6.5 percent or higher on two different tests means you have diabetes.
If the A1C test is not available, or if you have certain conditions - such as abnormal hemoglobin (known as the hemoglobin variant) - that interfere with the A1C test, your doctor will diagnose diabetes. The following tests can be used.
Random blood sugar test
Blood sugar values are expressed in deciliters (mg / dL) or millimoles (mmol / L) per liter. When you last eat, a blood sample showing that your blood sugar level is 200 mg / dL (11.1 mmol / L) or higher indicates diabetes, especially if you have signs and symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and excessive thirst.
Fasting blood sugar test
Readings below 100 mg / dL (5.6 mmol / L) are normal. Levels of 100 to 125 mg / dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol / L) are considered prebiotic. If your fasting blood sugar is 126 mg / dL (7 mmol / L) or higher in two separate tests, you have diabetes.
Oral glucose tolerance test
During pregnancy, this test is used less frequently than others. You should fast at night and then drink the sweet liquid in the doctor's office. Blood glucose levels are checked periodically for the next two hours.
Blood sugar levels below 140 mg / dL (7.8 mmol / L) are normal. Readings between 140 and 199 mg / dL (7.8 mmol / L and 11.0 mmol / L) indicate prebiotic. A reading of 200 mg / dL (11.1 mmol / L) or more after two hours indicates diabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends getting tested regularly for type 2 diabetes at age 45, especially if you are overweight. If the results are borderline, ask your doctor when to come for a second test.
Screening is also recommended for those over 45 years of age and overweight if they have a sedentary lifestyle, family history of type 2 diabetes, personal history of gestational diabetes, or risk factors for heart disease or diabetes such as hypertension above 140 /. 90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
If you are diagnosed with diabetes, doctors may perform other tests to differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes - because both conditions often require different treatments.
These steps can help keep your blood sugar levels back to normal, which can delay or prevent problems.
Weight loss
There is only a 5 to 10 percent difference in your body weight, however, losing 7 percent or more of your initial weight seems ideal. This means that anyone weighing 180 pounds (82 kg) will need to lose less than 13 pounds (5.9 kg) to have an effect on blood sugar levels. Controlling fractions and eating a healthy diet are early ways to lose weight.
Nutritious food
Contrary to popular belief, there is no specific diabetes diet. However, it is important to focus on your diet:
- Low calorie
- Low refined carbohydrates, especially sweets
- Low-fat diets
- More vegetables and fruits
- Foods high in fiber
A registered dietitian can help you formulate a meal plan that suits your health goals, food preferences, and lifestyle. She or she will teach you how to monitor your carbohydrate intake and how many carbohydrates to eat with your meals and snacks to keep your blood sugar levels more stable.
Physical activity
Everyone needs regular exercise for fitness and maintaining health, and people with type 2 diabetes are no exception. Consult your doctor before starting an exercise program. Enjoy activities like walking, swimming, and biking so you can make them a part of your daily routine.
Aim for at least 30 to 60 minutes of moderate (or 15 to 30 minutes of vigorous) aerobic exercise on most days of the week. The combination of exercise - aerobic exercise, walking, or dancing on most days, combined with resistance training, weightlifting, or doing yoga twice a week - offers more benefits than any other form of exercise.
Remember that physical activity lowers blood sugar. Check your blood sugar level before any action. If you are taking diabetes medications to lower your blood sugar, you should eat breakfast before exercising to prevent blood sugar.
It is also important to reduce the amount of time spent on passive activities such as watching TV. Try turning slightly every 30 minutes.
Monitors your blood sugar
Depending on your treatment plan, your blood sugar levels should be checked and recorded several times a day if you are on insulin. Ask your doctor how often you want to have your blood sugar checked. The only way to keep your blood sugar level within your target range is to carefully monitor it.
Diabetes medications and insulin therapy
Some people with type 2 diabetes can achieve their target blood sugar levels with diet and exercise, but most require diabetes medications or insulin therapy. Deciding which medications are best depends on a number of factors, including your blood sugar level and any other health issues you may have. Your doctor will combine different classes of drugs to help control your blood sugar in a variety of ways.
Examples of possible treatments for type 2 diabetes are:
Metformin (Glucophage, glumeta, others)
Generally, metformin is the first drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing the production of glucose in the liver and improving your body's sensitivity to insulin so that your body can use insulin more efficiently.
Side effects of metformin include nausea and diarrhea
These side effects can be eliminated when your body becomes addicted to medicine or if you take medicine with food. If metformin and lifestyle changes are not enough to control your blood sugar level, other oral or injected medications may be added.
Sulfonylurea
These drugs cause your body to secrete more insulin. Examples are glyburide (diabetes, Glynase), glyphosate (Glucotrol), and glimepiride (April). Side effects of low blood sugar and weight gain.
Meglitinides
These drugs - such as repaglinide (Prandin) and nucleotide (Starlix) - act like sulfonylureas by stimulating the pancreas to secrete more insulin, but they act faster and have a shorter duration in the body. . They are also at risk for low blood sugar and weight gain.
Thiazolidinediones
Like metformin, these drugs - including rosiglitazone (Avandia) and pioglitazone (Actos) - make body tissues more sensitive to insulin. These drugs are associated with weight gain and other serious side effects such as heart attack risk and anemia. Because of these risks, these drugs are usually not the first-choice treatment.
DPP-4 inhibitor
These drugs - sitagliptin (Januvia), saxagliptin (Onglija), and linagliptin (Tredgenta) - help lower blood sugar levels, but have very little effect. These do not cause weight gain, can cause joint pain, and increase the risk of pancreatitis.
GLP-1 receptor agonist
These injectable drugs slow down digestion and help lower blood sugar levels. Their use is often associated with weight loss. Possible side effects include nausea and increased risk of pancreatitis.
Examples of exenatide (beta, bidian), liraglutide (Victoza), and semaglutide (Olympic) GLP-1 receptor agonists. Recent research has shown that liraglutide and semaglutide reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke in people at high risk for those conditions.
SGLT2 inhibitor
These drugs prevent the kidneys from reabsorbing blood sugar. Instead, sugar is excreted in the urine. Examples are conaglyphosine (Inokana), dapaglyphosine (FARXIGA), and empagliflozin (Jordan).
Medications in this class of drugs reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke in those at high risk of those conditions. Side effects may include increased risk of vaginal yeast infection, urinary tract infection, low blood pressure, and diabetic ketoacidosis. Kenglyphosine, but not other drugs in the class Associates.
Top Homeopathic Medicines for Diabetes Mellitus
Abroma Augusta:One of the Best Homeopathic medicines for Diabetes with loss of flesh and weakness
Abroma Augusta is the top natural Homeopathic medicine to treat Diabetes Mellitus. Its use is highly recommended in those patients who are losing flesh and suffer from extreme weakness due to Diabetes Mellitus. The patients who can greatly benefit from this Homeopathic medicine have an increased thirst with dryness of mouth. They also have an increased appetite and the urination is very frequent day and night. Excessive weakness is felt after urination. Homeopathic medicine Abroma Augusta is also of great help in treating sleeplessness in a person with Diabetes. Another sphere in which this Homeopathic remedy yields good results is skin complaints like boils and carbuncles in a diabetic patient. Burning sensation in the whole body is a prominent general symptom that can be found in persons requiring Abroma Augusta.
Phosphorus- One of the best Homeopathic medicines for Diabetes with Weakness in Vision
Phosphorus is a natural Homeopathic medicine of great help for treating Diabetes Mellitus, though its use depends completely on the constitutional symptoms of the patient. Homeopathic medicine Phosphorus is a remedy of great help for weakness of vision in a diabetic patient.
Syzygium Jambolanum: Top Homeopathic medicines for reducing sugar levels
Syzygium Jambolanum is among the best natural Homeopathic remedies for the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. It acts promptly and efficiently in decreasing the sugar levels. Excessive thirst and excessive urination are always present in the patient. Homeopathic medicine Syzygium Jambolanum also gives wonderful results in treatment of long-standing ulcers in a diabetic patient.
Phosphoric Acid: One of the Homeopathic medicines for Diabetes with extreme weakness
Phosphoric Acid is an excellent natural Homeopathic remedy for extreme weakness, either mental or physical, in a diabetic patient. Such patients feel exhausted all the time. They have a weak memory and are forgetful. Some sort of history of grief may be found in patients requiring this Homeopathic medicine. For numbness of feet in patients of Diabetes Mellitus, Phosphoric Acid is the best Homeopathic remedy.
Gymnema Sylvestre: Homeopathic Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus with weight loss
Gymnema Sylvestre is a natural Homeopathic medicine of great help for patients of Diabetes Mellitus who are losing weight with weakness and exhaustion. In such patients, this Homeopathic remedy works as a tonic resulting in improvement of overall health. With Homeopathic medicine Gymnema Sylvestre,the patient puts on weight and feels energetic.
Best Homeopathic Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus
Homeopathic medicines for Diabetic Retinopathy (damage to eyes due to Diabetes)
Homeopathic medicines Phosphorus, Arnica, Belladona and Lachesis are equally good natural remedies to deal with eye complaints in diabetic patients. The most suitable Homeopathic medicine out of these is selected on the basis of symptoms described by each patient.
Homeopathic medicines for Diabetic Nephropathy (kidney damage due to Diabetes)
Natural Homeopathic medicines that can be very beneficial in the treatment of kidney damage are Lycopodium, Arsenic Album and Serum Anguillae. A complete case history is taken to select the suitable Homeopathic medicine out of these to deal with the kidney complications in diabetic patients. Homeopathy offers a small supportive role only in this condition and that too in early stages.
Homeopathic medicines for Diabetes with Neuropathy (nerve complaints like numbness in hands and feet)
To deal with the problem of numbness in feet and hands due to Diabetes,natural Homeopathic medicines Phosphoric Acid, Sulphur and Helonias are considered the best.
Homeopathic medicines for skin ulcers in diabetic patients
Skin ulcers is a very common complication in patients of Diabetes Mellitus. The diabetic skin ulcers are mostly formed on the feet. Natural Homeopathic medicines Syzygium Jambolanum and Secale Cornutum are excellent remedies to deal with ulcers in diabetic patients.
Homeopathic medicines for constipation in diabetic patients
For treating constipation in diabetic patients, Homeopathic medicines Carlsbad, Lac Defloratum and Natrum Sulph top the list. Which of these Homeopathic remedies best suits you is decided after taking note of the individual symptoms.
Homeopathic medicines for weak memory in diabetic patients
To improve the weak memory in patients of Diabetes Mellitus, Kali Phos, Nux Vom and Phosphoric Acid are the natural Homeopathic medicines of great help.
Homeopathic Medicines for Diabetes Mellitus with extreme weakness
The best natural Homoeopathic medicines to improve the general health of diabetic patients with extreme weakness are Arsenic Album, Phosphorus, Phosphoric Acid and Carbo Veg. Any one of these Homeopathic remedies can be of great help depending upon the individual symptoms of the patient.Homeopathic Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus can also be very effective in treating Erectile Dysfunction, which can be one of the serious consequences of longstanding Diabetes.
Conclusion:
Here is the massive guide that give you all the info about Diabetes, Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes. You can clearly see that how the types of diabetes is differ from each other. We mention each and every aspect regarding to diabetes. Now its upon you if you like all the info and it is up to your taste then please share it.
Regards: Dr. Naveed Shehzad