Bronchial
Bronchial
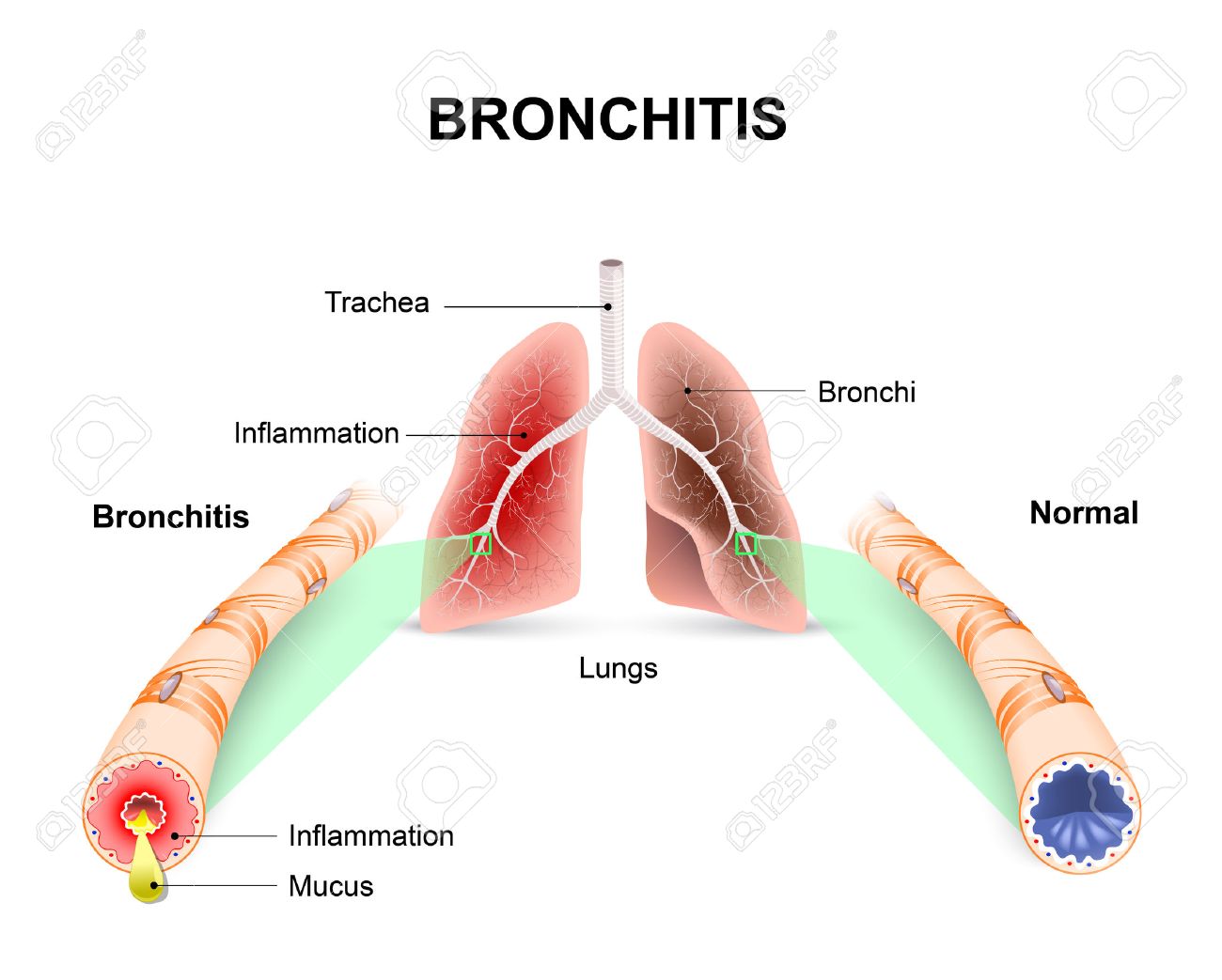
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your airways, which expels air from your lungs. People with bronchitis often have runny nose, which is blurred. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic.
It usually develops from a cold or other respiratory, acute bronchitis is more common. Chronic smoking, severe condition, persistent irritation or inflammation of the trachea, usually due to bronchial.
Symptoms for Bronchial
Whether it is acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, the signs and symptoms may include:
- Cough
- Production of mucus (sputum), which may be clear, white, yellow or green - rarely, filled with blood
- Fatigue
- Difficulty in breathing
- Mild fever and chills
- Chest discomfort
Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that lasts for at least three months and two years in a row. If you have chronic bronchitis, you may sometimes have a cough or other symptoms. In those cases, you may have a more serious infection than chronic bronchitis.
When to see a doctor
- It lasts over three weeks
- This will prevent you from falling asleep
- It is associated with fevers greater than 100.4 F (38 C)
- It produces radiant mucus
- It produces blood
- It is associated with shortness of breath
Acute Bronchial
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by bacteria, often the same bacteria that cause the common cold and flu. Antibiotics do not kill germs, so these types of medications do not help in most cases of bronchitis. Smoking is a very common cause of chronic bronchitis. Air or dust pollution or toxic gases in the atmosphere or at work can also contribute to this condition.
Regard: Dr. Naveed Shahzad