Goiter
Overview
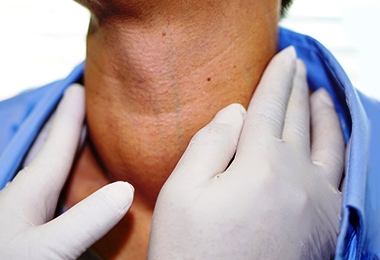
Goiter (GOI-tur) is an abnormal growth of your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland, which is present on the base of your neck. No doubt goiter is usually painless but if it's large in number may create difficulty in swelling.
Features
Not all garter causes signs and symptoms. But if you notice any of the sign or symptoms it maybe include:
- Feel tight in your throat
- Cough
- Blunt
- Difficult to swallow
- Difficulty in breathing
Being goiter means your thyroid gland is not functioning normally. Even when growing up, Many things can cause your thyroid gland to expand. The most common are:
Iodine deficiency
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones and is found mainly in seawater and coastal soils. In developing countries, people who live inland or at high altitudes often do not have iodine and goiters develop when the thyroid rises in an attempt to get more iodine. The goiter disease is mostly growing up when the thyroid gland produced more and more thyroid hormones.
Lonely thyroid nodules
This is one of the cases in which a single nodule produces in one part of your thyroid. Most nodules are non-cancerous and non-cancerous.
Thyroid cancer
it is much less common than benign thyroid. The biopsy of the thyroid nodules is very accurate in determining whether it is cancer.
Pregnancy
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) produced during pregnancy can slightly increase your thyroid gland. Goiters can affect anyone. They are congenital and can come at any time during their lifetime. Some common risk
factors for goiter are:
Dietary iodine deficiency
People living in areas with low iodine supply and no access to iodine supplements have a higher risk of goiter. Being a woman. Because women are at higher risk for thyroid disorders, they are more likely to get goiter. The guitar is most visible after the age of 40. A personal or family history of the autoimmune disease increases your risk.
Regard: Dr. Naveed Shahzad